Aortic Valve Stenosis Treatment In Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
Aortic stenosis is a condition where the aortic valve (the valve between the left ventricle and the aorta) becomes narrowed, restricting blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body. This can put a strain on the heart and lead to serious complications if not treated.
Aortic stenosis is a serious heart condition in which the aortic valve—the valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta—becomes narrowed.
This narrowing restricts the flow of oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body, forcing the heart to work harder to pump blood through the narrowed valve.
Over time, this added strain can weaken the heart muscle and lead to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and even fainting. If left untreated, aortic stenosis can result in life-threatening complications including heart failure.
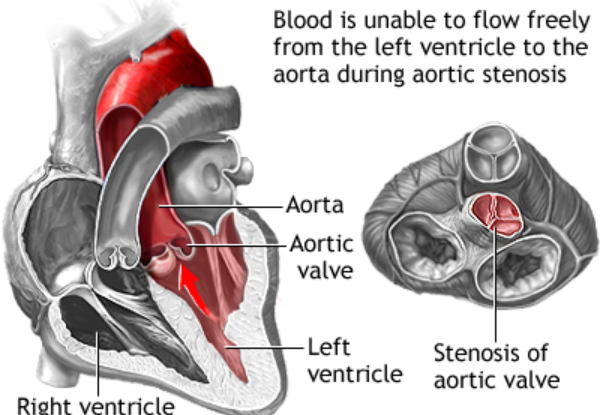
Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial to managing this condition effectively. Fortunately, patients now have access to advanced Aortic Valve Stenosis Treatment in Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, where a combination of skilled cardiologists, state-of-the-art facilities, and minimally invasive procedures like TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement) offer patients a chance at a healthier, more active life.
Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or seeking a second opinion, timely intervention can make all the difference.
Key Points:
Causes:
- Age-related calcification: The most common cause in older adults, where calcium deposits build up on the valve over time, causing it to stiffen and narrow.
- Congenital heart defects: Some individuals are born with a bicuspid aortic valve (having two leaflets instead of three), which can lead to stenosis.
- Rheumatic fever: A complication of untreated strep throat that can damage the heart valves, including the aortic valve.
Symptoms:
- Chest pain (angina), especially with exertion.
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, particularly during physical activity.
- Fatigue due to the heart's inability to pump blood efficiently.
- Fainting (syncope), often with exertion, due to insufficient blood flow to the brain.
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats.
Diagnosis:
- Echocardiogram: The most common test to assess the severity of the narrowing and examine the aortic valve’s function.
- Chest X-ray and ECG may be used to assess heart size and rhythm.
- Cardiac catheterization: In some cases, this test may be done to measure the pressure inside the heart chambers and the aorta.
Treatment:
- Medications: To manage symptoms, such as diuretics for fluid retention, but they don't cure the stenosis.
- Aortic valve replacement (AVR): In severe cases, surgery to replace the damaged valve with a mechanical or biological valve is often necessary.
- Balloon valvuloplasty: A procedure where a balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed valve (usually temporary and less common).
Complications:
- Heart failure: Due to the increased workload on the heart.
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms, especially atrial fibrillation.
- Sudden cardiac arrest: In severe cases, aortic stenosis can lead to sudden death, particularly if left untreated.
Aortic stenosis is a serious condition, and treatment often involves valve replacement when the condition becomes symptomatic. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Diagnosis:
- Echocardiogram: The most common test to assess the severity of the narrowing and examine the aortic valve’s function.
- Chest X-ray and ECG may be used to assess heart size and rhythm.
- Cardiac catheterization: In some cases, this test may be done to measure the pressure inside the heart chambers and the aorta.
Treatment:
- Medications: To manage symptoms, such as diuretics for fluid retention, but they don't cure the stenosis.
- Aortic valve replacement (AVR): In severe cases, surgery to replace the damaged valve with a mechanical or biological valve is often necessary.
- Balloon valvuloplasty: A procedure where a balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed valve (usually temporary and less common).
Complications:
- Heart failure: Due to the increased workload on the heart.
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms, especially atrial fibrillation.
- Sudden cardiac arrest: In severe cases, aortic stenosis can lead to sudden death, particularly if left untreated.
Aortic stenosis is a serious condition, and treatment often involves valve replacement when the condition becomes symptomatic. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Explore More : Heart Transplantation Surgery in Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
